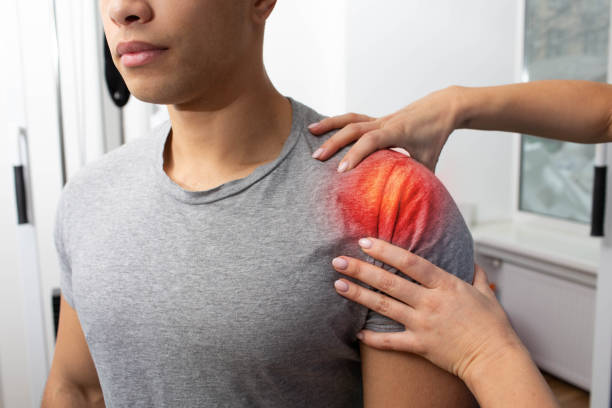
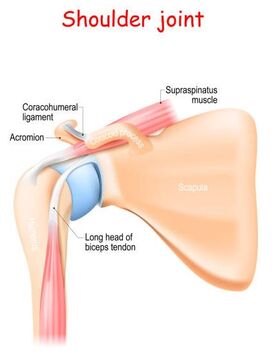
biceps tendinopathyBiceps tendinopathy refers to inflammation of the long head tendon of the biceps brachii. The Biceps brachii is a muscle located in our upper arm, and primarily contributes to movements such as flexion of the elbow and supination of the forearm (i.e., rotation of the forearm from a palm-down to palm-up position). Repetitive movements such as lifting, pulling, reaching, or throwing can lead to biceps tendinopathy or even tears of the upper biceps tendon. Biceps tendinopathy presents primarily as anterior shoulder pain, but is treatable with physiotherapy and exercise therapy. Biceps tendinopathy occurs when repetitive traction, friction, and shoulder rotation lead to inflammation in the tendinous portion of the muscle, located in the bicipital groove of the humerus. This causes the tendon to swell (or potentially hemorrhage), resulting in further mechanical irritation and predisposition to shear forces. Overtime, if left untreated, the tendon undergoes degenerative changes such as fibrosis, scarring, and the development of adhesions which compromise tendon mobility. In the most severe cases, the biceps tendon may eventually rupture. Fortunately, biceps tendinopathy is treatable with physiotherapy, exercise programming, and, in some severe cases, steroid injections or surgery. |
symptoms
|
causes
|
treatment
|